The goal of ERP software implementation is to improve corporate process efficiency while drastically lowering operating expenses. That is why it is critical for organizations to have a comprehensive ERP software pricing guide so that they can make the best decision.
The ERP software pricing guide provided below can help you minimize and control your overall cost of ownership, more efficiently manage your business resources, and enhance the return on your investment during the early stages of deployment.
In today’s competitive business environment, with exchange rate unpredictability, you must future-proof your organization and establish a solid, dependable base for growth.
What is an ERP system?
ERP stands for enterprise resource planning, but what exactly does that mean? ERP systems aid in the essential business activities required to run a firm, such as finance, human resources, manufacturing, supply chain, and others. At its most basic, ERP software aids in the efficient management of an integrated system by serving as a record of the entire system.
Even if ERP systems today are rudimentary and resemble ERP systems from decades ago. Today, the system is integrated with the cloud and cutting-edge technologies such as AI/ML to deliver intelligent automation and increased company efficiency. Modern cloud ERP software linked internal processes with enterprises all over the world, allowing corporations to maintain market agility and speed.
Traditional ERP VS SAP ERP
Modern SAP Cloud ERP aims to perform all that a traditional ERP does and more. SAP ERP centralizes data and communication in order to achieve complete integration of industrial components.
ERP Software Pricing Guide – SAP ERP modules
These features are frequently given as an add-on to a standard ERP system, and they are unquestionably expensive. However, with the current ERP setup and customization capabilities, it is straightforward to add applications through ERP implementation.
ERP appliances concentrate on a number of important business operations, with each trait having its own set of tools to avoid adding a solution with redundant functionality. It is critical to understand which of these is most advantageous to your organization. We attempted to cover everything in our ERP software grading guide so that you could comprehend it.
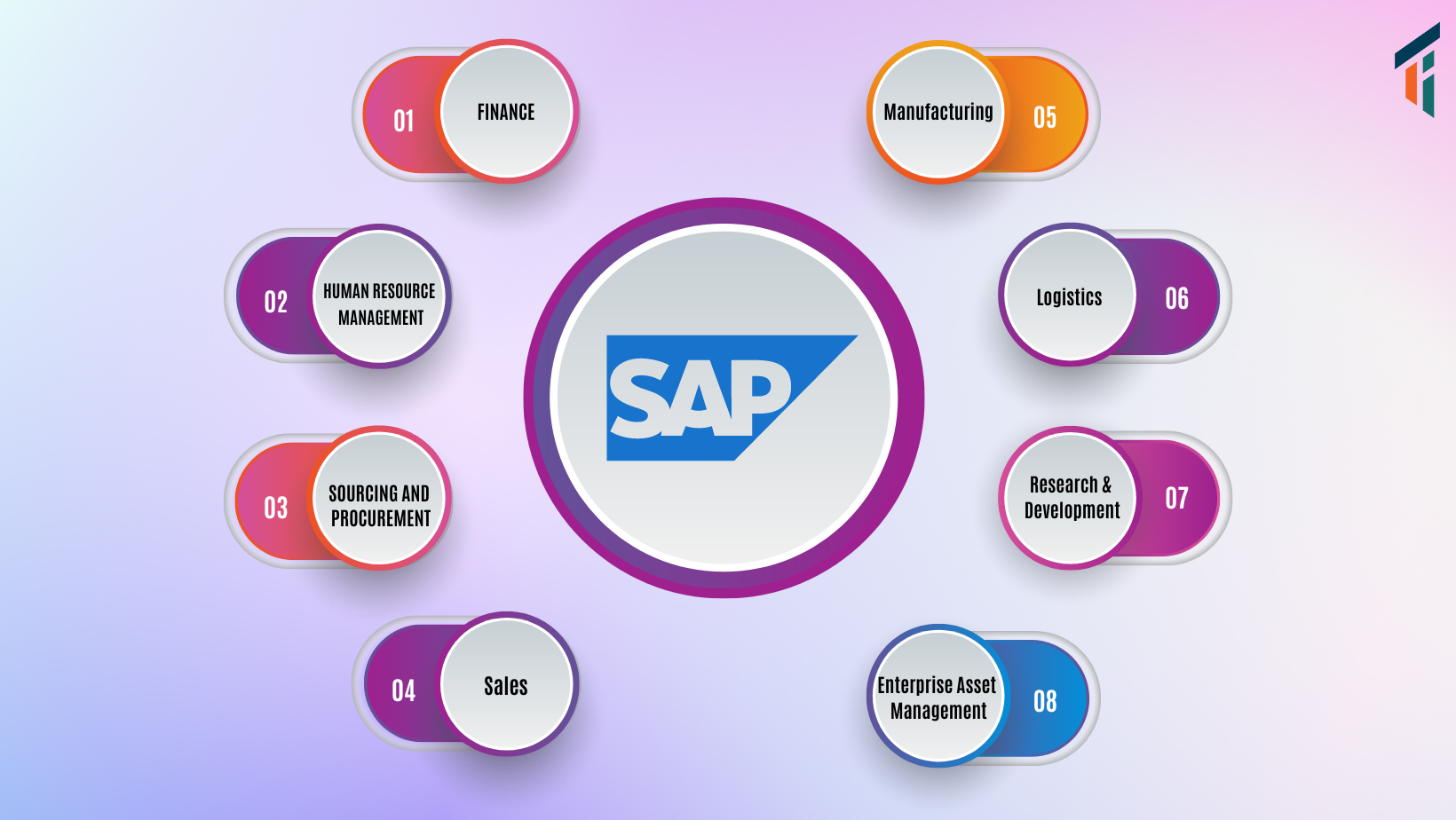
Let us look at some popular ERP modules.
1. Finance
Most ERP frameworks are built around the money and accounting module. In addition to dealing with the overall record and automating key monetary tasks, it assists organizations with following accounts payable (AP) and receivable (AR), closing the books proficiently, producing monetary reports, conforming to income acknowledgement guidelines, and limiting monetary risk, to name a few.
2. Human resource management
Most ERP frameworks include an HR module that provides centre capabilities including time, participation, and finance. Core items, or even entire human capital management (HCM) suites, can link with the ERP and provide more robust HR usefulness – everything from labour force investigation to executive worker experience.
3. Source and procurement
The sourcing and procurement module helps organizations receive the resources and services they need to manufacture their products – or the items they need to exchange. The module collects and automates purchasing, including demands for statements, contract generation, and endorsements.
It can reduce underbuying and overbuying, improve provider conversations using AI-powered data, and even be consistently associated with purchaser organizations.
4. Sales
The sales module tracks interactions with prospects and customers and assists reps in utilizing information-driven bits of knowledge to expand deals and target lead with relevant enhancements and upsells opportunities. It includes functionality for the request-to-cash process, such as requests to executives, contracts, charging, deal execution to the board, and deal force assistance.
5. Manufacturing
The assembling module is an essential aspect of ERP programming’s planning and execution. It supports organizations in improving complex assembly processes and ensuring creation is in accordance with requests. This module frequently incorporates usefulness for material needs planning (MRP), creation booking, fabricating execution, and quality administration, and that’s only the tip of the iceberg.
6. Logistics
Another critical component of ERP systems, the inventory network module monitors the movement of merchandise and supplies throughout an organization’s shop network. The module provides devices for continuous stock management, warehouse jobs, transportation, and strategies – and can aid in increasing the perceptibility and versatility of the production network.
7. Research and development
This module provides tools for item planning and development, product lifecycle management (PLM), product consistency, and much more – allowing organizations to make new advancements quickly and affordably.
8. Enterprise asset management
Effective ERP systems can include an EAM module, which helps resource-constrained organizations manage free time and keep their PCs and hardware functioning at peak efficiency. This module includes applications for predictive maintenance, booking, resource activities and planning, climate, environment, health and safety (EHS), and much more.
Unlock Your success with Our Top-Notch Formula for Guaranteed Growth!
ERP Software Pricing Model
Any cost concerns in the case of ERP system price models are a daunting problem for the first time you acquire or upgrade from one platform to another. Consider a purchase that shows a scale of enterprise to ensure that it has an effective value since its application.
Nonetheless, in today’s typical ERP, the two most essential and widely recognized ERP modules are on-premise systems and the SaaS model, sometimes known as cloud-based. However, when it comes to these models, each has its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
ERP licensing
Small businesses using local server ERP licenses averaging $20k, in addition to foundation costs, can investigate for a variety of reasons, as any underlying buy expense can normally be recovered quickly, and once paid for, additional downstream personal funds can be opened up for use somewhere else.
This strategy is often useful for organizations that manage and operate their own small companion exchange networks, such as ERP-managed point-of-sale (POS) systems for basic grocery stores.
In this case, fundamental trades can travel directly from at least one of the store’s POS terminals(s) to a privately facilitated server, without the need to connect with any other larger organization.
However, in this case, the primary limitation of this ERP estimating model would be limited development, as the project will need to add more framework to keep aware of development beyond its fundamental design. The underlying cost can also be a barrier for private ventures with little free cash.
ERP SaaS subscription
SaaS or cloud-based ERP execution provides an especially good benefit for medium-sized or large-scale private/public organizations (using $20m as a common starting expense benchmark). In this case, a reasonable permit purchase of $40k, in addition to the framework, might enable an endeavour to recover its hard expenditures in only two company years, leaving only month-to-month authorizing expenses to manage going forward.
This is especially advantageous if a business needs to expand quickly in order to accommodate more asset management sooner, as one could see with a group of new agreements. This potential for growth also makes SaaS membership ERP pricing models appealing to smaller businesses looking to expand.
What is the price of an ERP system in the UK? A Comprehensive ERP Software pricing
Cloud ERP typically provides cheaper expenses than on-premise ERP because there is no equipment to purchase – and no expensive in-house IT specialists to hire. The merchant handles the service and charges the client a yearly or monthly membership fee, which is usually based on the number of clients.
When calculating the return on investment (ROI) and total cost of ownership (TCO) of another ERP implementation, the underlying and continuing labour force expenses are just as important as the product selection and organizational costs. New variables should be considered while selecting cloud and cross-breed options.
For example, maintenance, computer capacity, downtime, recovery, security, privacy, and other operational expenditures. Let us explore ERP software prices for small and large organizations.
ERP pricing for small businesses in the UK
As a business executive, the correct ERP can deliver a plethora of benefits to your small business strategy, including:
Reduced stock cost through improving stock perception and tracking stock.
Real-time tracking and analytics tools to aid long-term planning.
Improved business security through dedicated insurance for on-premise/cloud systems.
Client data is unified, making it simple to retrieve reports and fix issues.
Process automation allows for faster billing and regulatory compliance.
ERP software pricing for Enterprise in the UK
Enterprises require high-quality ERP systems. Companies with more than 501 employees and a revenue of more than $250 million should be prepared to spend more than $1 million on such a tool.
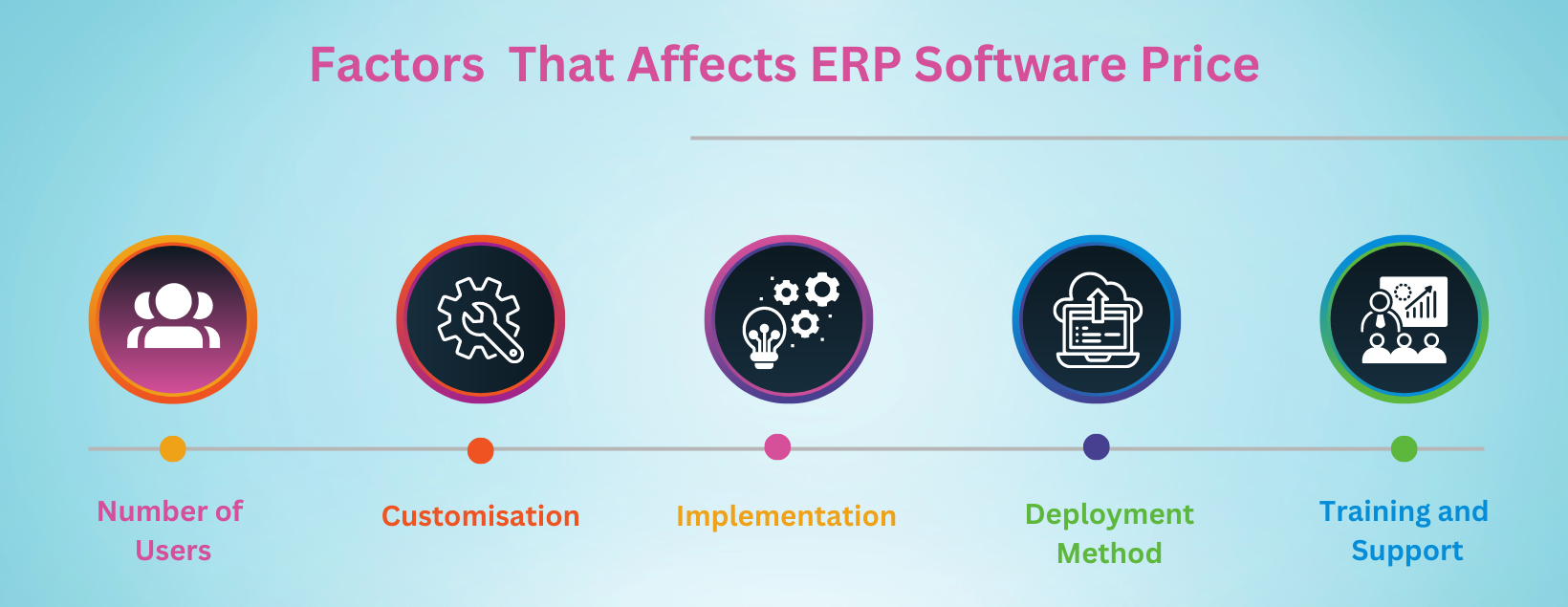
Factors affecting the ERP software pricing
Everyone in the SME industry is aware of how much ERP costs. What they cannot refute is that ERPs, albeit a profitable endeavour, are not a one-time investment. Furthermore, even if the implementation is successful, there is no clarity.
Number of the users
When selecting an ERP package for your company, you should consider the number of customers who will initially approach the product. Many ERP vendors charge on a per-client basis, which means that the more people who use it, the more expensive it becomes.
You must also account for the cost of adding new clients to your framework. How that cost may rise in the future as your company grows.
You’ll need to check with the specific ERP you’re interested in to see if they charge per client. This is important, especially if you have a large number of staff who will need access since the prices will pile up.
Customization
ERP customization is less expensive. For that reason, finding a product/arrangement that meets all of your immediate needs is critical. Many retailers offer reconciliations with third-party supplementary items or the option to recall explicit modules for extended program usefulness.
The cost of these extra features varies depending on what you want to include and which merchant you choose for your base bundle. This factor, along with ERP cost, should be considered.
Implementation
Most SMEs face a slew of challenges when it comes to ERP implementation, as these frameworks are designed for large organizations that are not new to the concept of digitization. If you are executing ERP intriguingly, you will most likely demand more dedicated specialized aid than an organization that has experience sending this type of software.
Deployment method
Both of these organizational strategies have advantages and disadvantages, with direct instalment being one advantage that makes cloud arrangement more appealing to certain organizations. If you’re more interested in an on-premise option, keep in mind that the upfront costs are higher.
Because of the additional items/customization, organizations using cloud ERP find up paying a high cloud ERP pricing without knowing if the framework was successfully implemented or not.
Training and support
Training and customer support are two critical aspects to consider when determining the cost of an ERP solution and how well a program will perform with your organization’s needs. Overall, 15-20% of a product’s budget, makes it a significant chunk of your cost consideration when calculating ERP costs.
Some retailers provide their own preparation options on-site as well as through online instructional exercise records and classes. However, depending on the retailer you choose, this assistance may be remembered for your overall programming expense.
How to Select the Best ERP Pricing Model – A Comprehensive ERP Pricing Guide
Regardless of whether you have clearance to put resources into another ERP software, you need to make a budget and justify the costs. While not all of these components will apply to all executions, they should be considered in order for you to complete the ERP decision process for your firm.
Here are a few important factors to consider while budgeting for ERP:
- Expenses for ERP software licensing
- Additional servers and hardware are required.
- Data transformation and migration to a new ERP system
- Customization may be required if necessary.
- Testing
- Training
- After-sales support from the vendor
These are the most important expenses to keep in mind for your budget, but you should also plan for financial hiccups and allow for contingencies. We’ll get into the hidden costs a little later.
ERP Selection as per business needs
Any cutting-edge ERP framework will have a large number of capacities based on the businesses they support and the modules they provide. However, there are ten major components that every project asset the board frameworks must include:
Common data: Centralized data and a single version of reality provide predictable, shared knowledge and a cross-functional view of the organization.
Embedded analytics: Built-in research, self-administration BI, detailing, and consistency apparatuses that can convey insightful knowledge for any business area.
Data perception: Dashboards, KPIs, and point-and-click inspection of essential data aid in quick and informed travel.
Automation: Automation of mundane tasks, as well as cutting-edge RPA managed by AI and AI.
UX/UI: Modules have a consistent look and feel, and process configuration and personalization tools are straightforward to use.
Integration: Continuous integration of business cycles and work processes, as well as open and simple reconciliation with other programming setups and information sources, including those from third parties.
New tech: AI and AI support, computerized companions, IoT, RPA, security and protection, and portability are all available.
Innovation stage: A rapid, proven, and stable innovation stack for this protracted conjecture, including a low-code/no-code stage.
What Is the Cost of ERP Implementation? – ERP Implementation and Installation Costs
Introducing the actual product will vary from one supplier to another and from one venture to another, particularly if you are going with an on-premise model but do not yet have enough foundation to support it. To fully appreciate establishing charges, you should examine your current foundation to see if it compares to facilitating the product and then determine the prices of the extension.
The ongoing cost to consider
Staff training, unforeseen customization, and data change are the most well-known undervalued or blatant costs of ERP adoption. You may reduce a major portion of the ‘hidden costs’ by anticipating the additional effort, preparation, and inclusions that your new ERP will necessitate. In any event, there are other costs that will emerge later, after execution, for which you must plan.
As a result, retraining may be required, resulting in additional time and assets that you had not planned. Regardless, there are frequently hidden benefits to execution that will offset the costs, and having approximately 10% possible spending plan factored into your ROI estimates will put you in a good position for any unexpected consumption.
Seven smart cost strategies for an ERP Software
By discussing the ERP software pricing guide, we also discussed these seven smart cost strategies that will assist small businesses and corporations in selecting the correct ERP software for their needs.
Select the Right Software
You should start by determining what you truly require in an ERP software system. Whatever solution your company chooses, the key to success is selecting a system based on your specific needs rather than focusing on all the capabilities you may never use.
If you are small to mid-sized firm with limited resources and budget, you may desire a fully integrated ERP system that is flexible enough with functions to adapt to your company’s ever-changing needs. This type of software will increase productivity at a considerably lesser cost.
Select the right deployment
The deployment of an ERP solution for your organization will be determined by a variety of factors, but you should prioritize the one that focuses on cost reduction. Software is available for both on-premise and cloud deployment.
The difference between the two is that you pay for on-premise ERP software as well as the cost of hardware setup and maintenance, whereas cloud services are often supplied on a software-as-a-service (SaaS) basis for a fixed monthly fee.
Follow a defined methodology
An expert ERP vendor will understand your business requirements and propose a proven implementation process. Using a pre-defined and organized implementation process decreases the risk and time wasted in monitoring and regulating the project, particularly during the execution phase.
This method also aids in keeping the project from slowing needlessly by focusing on the most crucial tasks.
Use concurrent licensing
Select limited licenses. User licenses for ERP software are typically charged on a concurrent basis, which means you don’t have to pay for all users, but only those that use the system at the same time. In this manner, you can cut costs by just paying for people who log in at the same time.
Purchase only useful modules
Purchasing modules that aren’t valuable to your organization at all or only in minor ways can have an impact on overall pricing. For example, your company will require a complex e-commerce module to meet its requirements, but it is not yet ready to employ those capabilities. Wait until you are ready, then add it to your agreement.
Control maintenance cost
Software maintenance entails maintaining the system up to date with essential improvements and zero errors. It can be costly to not maintain your ERP system updated or to leave issues unsolved for an extended period of time. You should obtain a service agreement from your ERP vendor to ensure regular upgrades and updates that will save you time and money in the long term.
Follow the Train the Trainer approach
Training every system user can raise total costs. Instead, teach a few of your top staff and assign them the responsibility of training additional users. This allows those important people to have a better and deeper grasp of the program, saving you money on additional training and reducing future reliance on your ERP supplier.
To wrap it up
You have probably learned how to estimate the costs of ERP establishment at this point. Various factors influence the overall cost of the ERP architecture. For a reasonable estimate, put ERP execution and support costs at one to two per cent of the organization’s annual revenue.
Understanding your organization’s squeezing requirement for various ERP modules is the best path to effective ERP execution, according to this ERP software pricing guide. Make assured that you only select modules that you absolutely need.
Target Integration understands where your industry’s future is headed and will give the greatest software solution for your needs. With ERP systems, we assist SMEs in reducing costs, lowering overheads, and increasing profitability.